Spammers are enemies of all sysadmins, because they are altering their tactics day by day. Keeping softwares up-to-date on your servers is not always as easy and solvable as we might think. Even though you have the latest application which is protected against the known security risks, you can have a lot of user-related contents which are like honey for hackers.
In case of a hosting provider, lots of customers use shared resources. Unfortunately, they often lack knowledge on how to keep their website up-to-date. You can send them tons of e-mails about the importance of strong passwords or raise attention to the significance of continuous security updates, if it is ineffective – and often it is – the conclusion is that, you have to protect their websites by yourself instead of them. Furthermore, some customers will be angry about these kinds of mails or simply become frightened and move their sites to the concurrent provider instead of patching the code.
Outdated content management systems, their themes and plugins are popular targets for spammers. Attempts below are from the same IP and reflect how spammers’ tactics have changed in the last 1-2 years. And it’s just one example from many many different kinds.
A typical spam attempt from about 1.5 years ago:
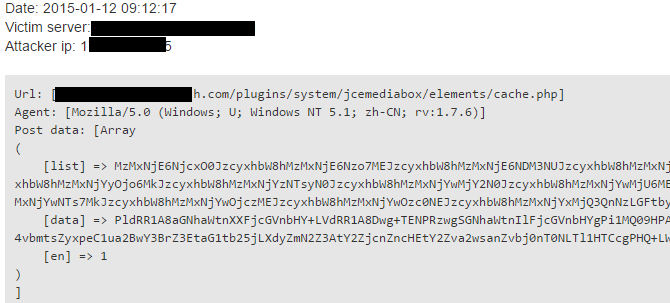
It was interesting to decode ‘list’ and ‘data’ HTTP GET parameters then discovering the regular sequences. After we base64 decoced them, first thing we realized the “,amo” sequence in the string.
33161:671;Bss,amo!33161:7:;0Bss,amo!33161:4375Bss,amo!33161;2:46Bss,amo!3316623;14Bss,amo!
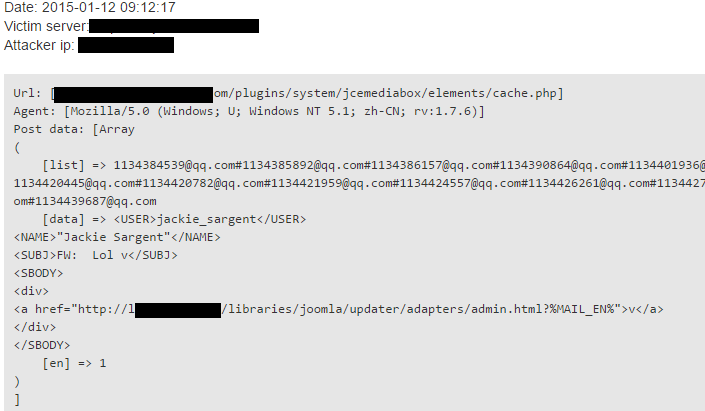
Our CEO, George said he had seen this before, as the encoded form of .com domain TLD, then we began to decode the whole text. The result was a list of e-mail addresses with hashmark delimiters between them.
The attacker often operates simple rotation or XORing with a constant key, and after a while, you can realise, these parameters are input of a spammer script, namely e-mail addresses and spam contents.
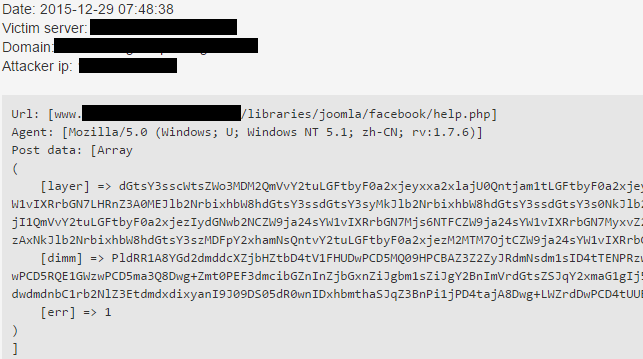
As sysadmins created different kinds of rules to reject these attempts, spammers’ tactics have changed and switched ‘list’ and ‘data’ to ‘layer’ and ‘dimm’ respectively, but the encoding remained the same.
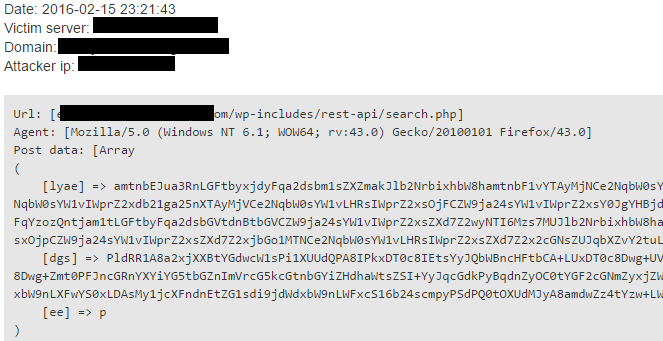
Clearly visible, simple pattern matching is beating the air. These keys can be various. Just take a look at the next example, where parameters are totally random and currently this is the common practice.
So, what can we do? Prevention is the basis of all defense, you have to stop spammers at an early stage. BitNinja has an up-to-date database with spammer IPs and it can help to discover scripts on your server that spammers are trying to use.



